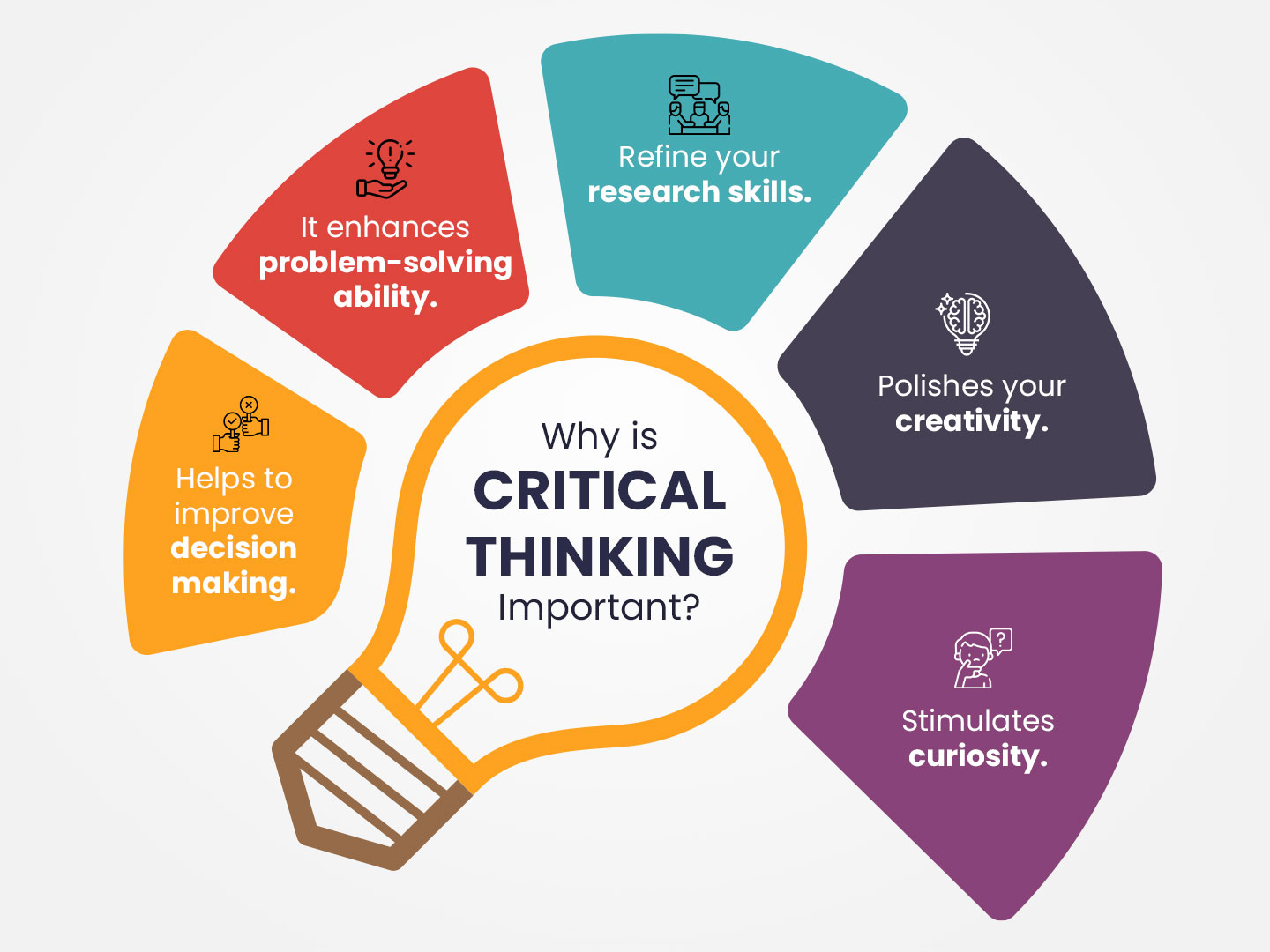
Critical thinking is a fundamental skill that prepares students for academic success and real-world challenges. In this article, we’ll explore strategies for educators to teach critical thinking effectively in the classroom.
Introduction:
Critical thinking is the ability to analyze, evaluate, and solve problems systematically. Educators play a vital role in developing this skill in students. Here are strategies for teaching critical thinking effectively:
- Questioning and Inquiry:
Encourage students to ask questions and explore topics from different angles. Open-ended questions spark curiosity and promote critical thinking. - Problem-Based Learning:
Use problem-based learning approaches where students tackle real-world issues and devise solutions. This fosters critical thinking and practical problem-solving skills. - Socratic Questioning:
Employ the Socratic method by asking thought-provoking questions that encourage students to examine their assumptions and reasoning. - Analyze and Evaluate Sources:
Teach students to critically assess information sources, including online content, to distinguish between reliable and unreliable information. - Deconstruct Arguments:
Help students break down arguments into their component parts, identifying premises, conclusions, and assumptions. - Creative Thinking:
Encourage creative thinking alongside critical thinking, as it can lead to innovative solutions and perspectives. - Mindful Reflection:
Promote mindful reflection, where students consider their thought processes and cognitive biases. - Collaborative Learning:
Collaborative group work can enhance critical thinking as students share and evaluate different ideas and perspectives. - Ethical Considerations:
Discuss ethical considerations in problem-solving and decision-making, helping students understand the broader implications of their choices. - Real-World Application:
Connect critical thinking to real-world scenarios and applications, demonstrating its practicality and relevance.
Case Study: The Philosophy for Children Program
The Philosophy for Children (P4C) program is an example of how critical thinking can be taught to students. It involves philosophical discussions and encourages students to think critically about philosophical questions and ethical dilemmas.
Conclusion:
Teaching critical thinking is a fundamental aspect of education. By using strategies such as inquiry, problem-based learning, Socratic questioning, and ethical considerations, educators can nurture critical thinking skills in students.